Diabetes is a prevalent disease affecting people across all age groups. The most prevalent form is Type 2 diabetes. Multiple treatment options are available to manage the disease effectively, ensuring a healthy life and preventing further complications.
In today’s corporate medical industry, finding old fashioned personalized healthcare care can be challenging. Recognizing this need, the experienced medical professionals at Hartland Medicine provide big healthcare experience with small practice attention to each patient. Contact us and schedule an appointment with a board certified doctor for diabetes treatment today.
Diabetes occurs when your blood sugar (glucose) levels are excessively high. This happens when your pancreas either does not produce sufficient insulin, fails to produce any at all, or your body doesn’t react appropriately to insulin’s effects. While most types of diabetes are chronic, meaning they last a lifetime, all forms can be managed with the help of medication and/or lifestyle adjustments.
There are several categories of diabetes, the most common ones include:
Type 2 Diabetes
In this form, your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or the body’s cells fail to respond to insulin correctly (insulin resistance). This type is the most prevalent, typically affecting adults, although children can also be diagnosed with it.
Prediabetes
This is a precursor to Type 2 diabetes, where your blood glucose levels are elevated but not high enough for a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
Type 1 Diabetes
This autoimmune disease leads to your immune system attacking and destroying insulin-producing cells in your pancreas for unknown reasons. Approximately 10% of individuals with diabetes have Type 1. It’s typically diagnosed in children and young adults but can develop at any age.
Gestational Diabetes
This form of diabetes occurs in some individuals during pregnancy. It usually subsides post-pregnancy, but those with gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Symptoms of diabetes encompass:
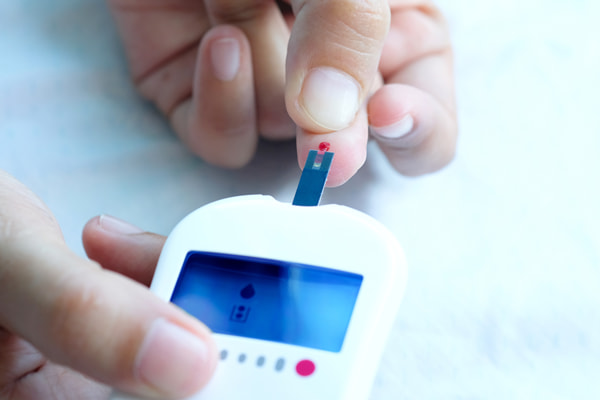
Diabetes is diagnosed by assessing your glucose level via a blood test. There are three tests to measure your blood glucose level:
An oral glucose tolerance test is ordered to screen for and diagnose gestational diabetes.
The prognosis or outlook for diabetes greatly depends on various factors, including:
In the United States, diabetes is the eighth leading cause of death, with a significant number of diabetes patients dying from heart attacks or strokes.
